%%capture
!pip install kornia
!pip install kornia-rsDenoise image using total variation
Advanced
Denoising
In this tutorial we are going to learn how to denoise an image using the differentiable
total_variation loss.
import io
import requests
def download_image(url: str, filename: str = "") -> str:
filename = url.split("/")[-1] if len(filename) == 0 else filename
# Download
bytesio = io.BytesIO(requests.get(url).content)
# Save file
with open(filename, "wb") as outfile:
outfile.write(bytesio.getbuffer())
return filename
url = "https://github.com/kornia/data/raw/main/doraemon.png"
download_image(url)'doraemon.png'import kornia as K
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
import torchvisiondef imshow(input: torch.Tensor):
out = torchvision.utils.make_grid(input, nrow=2, padding=5)
out_np = K.utils.tensor_to_image(out)
plt.imshow(out_np)
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()# read the image with kornia and add a random noise to it
img = K.io.load_image("doraemon.png", K.io.ImageLoadType.RGB32) # CxHxW
noisy_image = (img + torch.normal(torch.zeros_like(img), 0.1)).clamp(0, 1)
imshow(noisy_image)
We define the total variation denoising network and the optimizer
# define the total variation denoising network
class TVDenoise(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, noisy_image):
super().__init__()
self.l2_term = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction="mean")
self.regularization_term = K.losses.TotalVariation()
# create the variable which will be optimized to produce the noise free image
self.clean_image = torch.nn.Parameter(data=noisy_image.clone(), requires_grad=True)
self.noisy_image = noisy_image
def forward(self):
return self.l2_term(self.clean_image, self.noisy_image) + 0.0001 * self.regularization_term(self.clean_image)
def get_clean_image(self):
return self.clean_image
tv_denoiser = TVDenoise(noisy_image)
# define the optimizer to optimize the 1 parameter of tv_denoiser
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(tv_denoiser.parameters(), lr=0.1, momentum=0.9)Run the the optimization loop
num_iters: int = 500
for i in range(num_iters):
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss = tv_denoiser().sum()
if i % 50 == 0:
print(f"Loss in iteration {i} of {num_iters}: {loss.item():.3f}")
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()Loss in iteration 0 of 500: 3.081
Loss in iteration 50 of 500: 2.723
Loss in iteration 100 of 500: 2.359
Loss in iteration 150 of 500: 2.064
Loss in iteration 200 of 500: 1.828
Loss in iteration 250 of 500: 1.642
Loss in iteration 300 of 500: 1.497
Loss in iteration 350 of 500: 1.384
Loss in iteration 400 of 500: 1.297
Loss in iteration 450 of 500: 1.229Visualize the noisy and resulting cleaned image
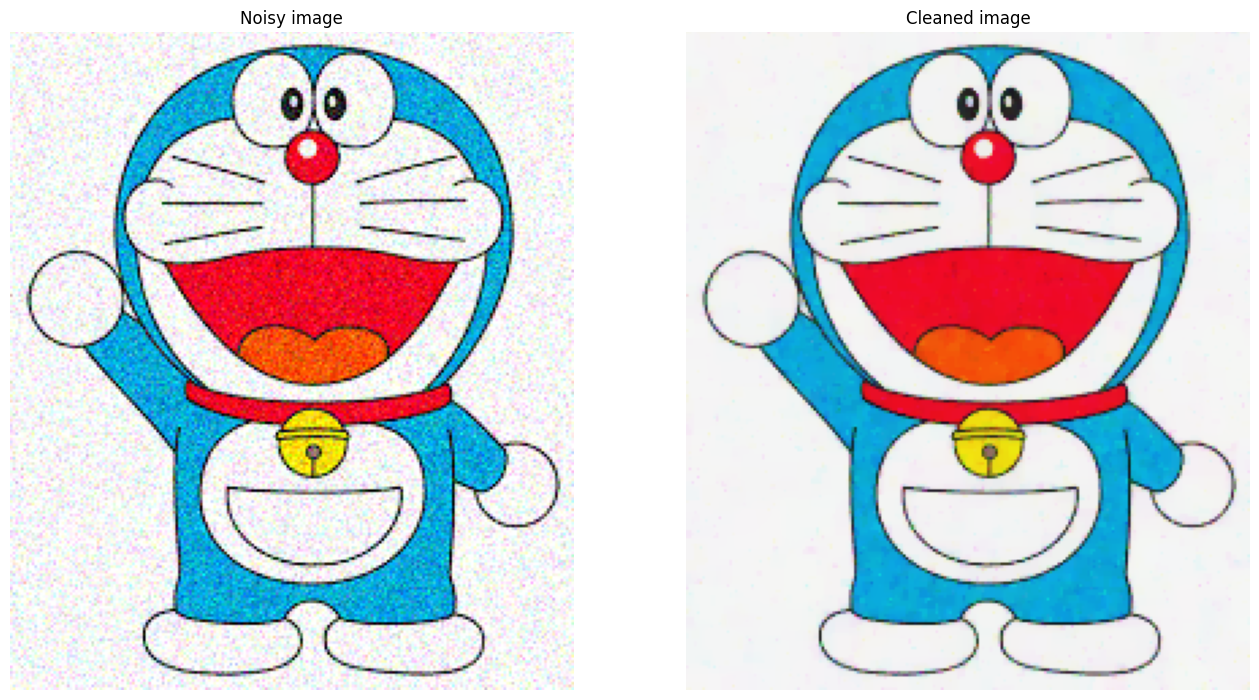
# convert back to numpy
img_clean = K.utils.tensor_to_image(tv_denoiser.get_clean_image())
# Create the plot
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(16, 10))
axs = axs.ravel()
axs[0].axis("off")
axs[0].set_title("Noisy image")
axs[0].imshow(K.tensor_to_image(noisy_image))
axs[1].axis("off")
axs[1].set_title("Cleaned image")
axs[1].imshow(img_clean)
plt.show()